Lipid Disorders
Introduction to Lipid Disorders (Hyperlipidemia)
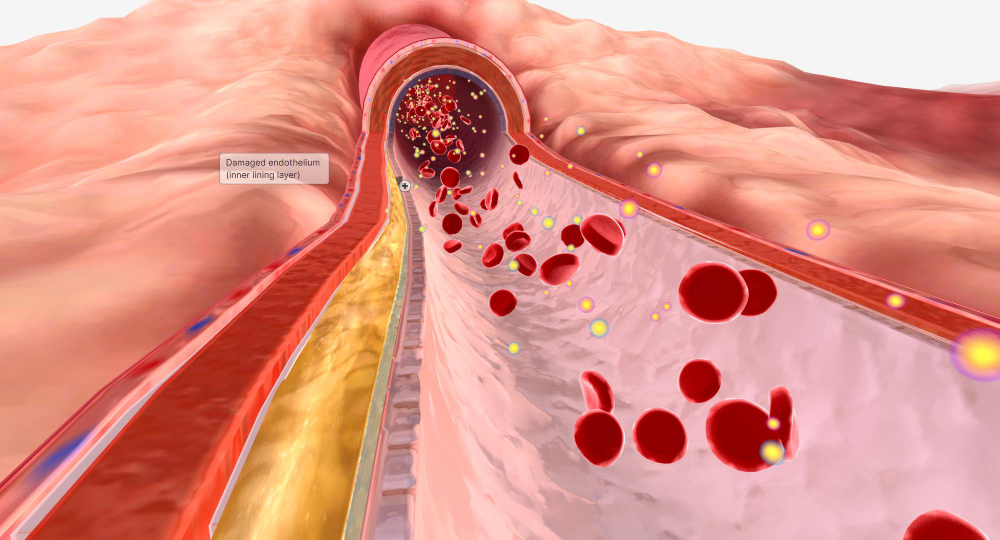
Lipid disorders, commonly known as hyperlipidemia, involve abnormal levels of lipids (fats) in the blood. Lipids include cholesterol and triglycerides, which are essential for normal body function but can cause health issues when present in excessive amounts. Hyperlipidemia is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including heart attack and stroke.
Understanding Lipids
Types of Cholesterol
- Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL): Often referred to as “bad” cholesterol, LDL carries cholesterol to tissues, where it can build up in the walls of arteries, leading to atherosclerosis.
- High-Density Lipoprotein (HDL): Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove cholesterol from the bloodstream, transporting it to the liver for excretion or reuse.
- Very Low-Density Lipoprotein (VLDL): Transports triglycerides and can contribute to plaque buildup in arteries.
Triglycerides
Triglycerides are a type of fat found in the blood. The body uses them for energy, but high levels can increase the risk of heart disease.
Causes and Risk Factors of Hyperlipidemia
Genetic Factors
- Familial Hypercholesterolemia: An inherited condition causing extremely high LDL cholesterol levels from a young age.
Lifestyle and Environmental Factors
- Diet: High intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol can increase lipid levels.
- Obesity: Excess body weight is often associated with higher levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
- Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise can lead to higher LDL and lower HDL cholesterol levels.
- Smoking: Increases LDL cholesterol and lowers HDL cholesterol.
Medical Conditions
- Diabetes: Can contribute to higher triglyceride and lower HDL cholesterol levels.
- Hypothyroidism: Underactive thyroid can lead to high cholesterol.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Can affect lipid metabolism.
Symptoms of Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia itself often presents no symptoms and is usually detected through blood tests. However, long-term unmanaged hyperlipidemia can lead to symptoms related to cardiovascular disease, such as:
- Chest Pain (Angina): Due to reduced blood flow to the heart.
- Xanthomas: Yellowish deposits of cholesterol under the skin, often seen in familial hypercholesterolemia.
- Pancreatitis: Severe abdominal pain from high triglyceride levels.
Diagnosis of Hyperlipidemia
Lipid Profile Test
A lipid profile test measures total cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and triglycerides. It is typically done after fasting for 9-12 hours to ensure accurate results.
Additional Tests
- Liver Function Tests: To rule out liver diseases affecting lipid metabolism.
- Thyroid Function Tests: To check for hypothyroidism.
- Blood Glucose Tests: To detect diabetes or prediabetes.
Treatment Options for Hyperlipidemia
Lifestyle Modifications
- Healthy Diet: Emphasize fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Reduce intake of saturated fats, trans fats, and cholesterol.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity per week.
- Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight to improve lipid levels.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking improves HDL cholesterol and overall heart health.
Medications
- Statins: Lower LDL cholesterol by inhibiting an enzyme involved in its production.
- Ezetimibe: Reduces the absorption of cholesterol from the intestine.
- PCSK9 Inhibitors: Monoclonal antibodies that significantly lower LDL cholesterol.
- Fibrates: Primarily reduce triglyceride levels and can increase HDL cholesterol.
- Niacin: Lowers LDL and triglycerides while raising HDL cholesterol.
Complications of Untreated Hyperlipidemia
Atherosclerosis
High levels of LDL cholesterol can lead to the buildup of plaques in the arteries, causing them to harden and narrow. This process, known as atherosclerosis, increases the risk of:
- Heart Attack: Blockage of coronary arteries can restrict blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Stroke: Blockage of arteries supplying blood to the brain.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Reduced blood flow to limbs, causing pain and mobility issues.
Pancreatitis
Extremely high triglyceride levels can cause inflammation of the pancreas, leading to severe abdominal pain and other complications.
Preventing Hyperlipidemia
Regular Screening
Routine blood tests to monitor cholesterol and triglyceride levels can help detect hyperlipidemia early. Adults should have their lipid levels checked every 4-6 years, or more frequently if they have risk factors.
Healthy Lifestyle Choices
- Balanced Diet: Focus on a diet low in saturated fats and high in fiber.
- Physical Activity: Regular exercise helps maintain healthy lipid levels and overall cardiovascular health.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Not smoking or quitting smoking reduces the risk of lipid disorders and cardiovascular diseases.
